Electronic contamination is a serious problem nowadays which affects a lot of countries and the people within them. It generates diseases, that can be mortal, and it also harms the environment. We investigated the impact that this problem generates in Argentina and we found that it is the third country in South America, followed by Mexico and Brazil, that generates the most electronic waste with around 300 thousand tons generated per year in a total of 41.8 million tons worldwide. The materials that compose the batteries for these electronics that are discarded turn toxic once they reach their estimated life. We took into account that the majority of people are used to throwing those products once they turn obsolete or break when the best solution for that kind of situation would be to recycle or reuse them in a way. Given that half of these products are thrown into open-air garbage dumps it is inevitable to think that they are going to contaminate. For this reason, we decided to confront this problematic, first by analyzing which are the components that turn toxic and then looking for possible solutions that would help us battle this problematic.
Problematic
When we began investigating the environmental impact that electronic products have over the environment we realized that this was a serious matter. E-waste posses components such as lead, mercury, cadmium, selenium, arsenic, and lithium among others. These six components are inoffensive during the life period of the devices, due to them being contained by plaques, circuits, connectors or cables but once they are discarded in landfills they react with water and organic matter, liberating toxics to the ground and to the sewers. Due to its non-biodegradable nature, these wastes are dangerous to the environment and the health of people.
The main problem that Argentina has is the quantity of waste in general that is produced in a year and how that contaminates. This waste is not separated nor treated and the fact that they are exposed to the sun, because of being in open-air garbage dumps, and other toxics makes them react with one another resulting in even more contamination.
- Cadmium: affects mainly kidneys and bones
- Mercury damages the central nervous system
- Hexavalent chromium: carcinogenic (tumors).
- Polyvinyl chloride (PVC) releases highly toxic dioxins and furans.
- Nickel in its oxidized, sulfated or soluble form causes cancer and Respiratory problems
- Zinc also affects health.
- Lithium can cause respiratory failure
Objective
The main objective that we are looking for is to mitigate the damage that we are dealing with our ecosystem. By starting with the municipality, recycling or trying to reuse waste before discarding it. Beyond that, we are looking for ways in which we can make people aware of the damage that these wastes are causing to the environment and that we have to act as fast as we can or else this will turn out to be a irredeemable damage.
EcoHorno
Process
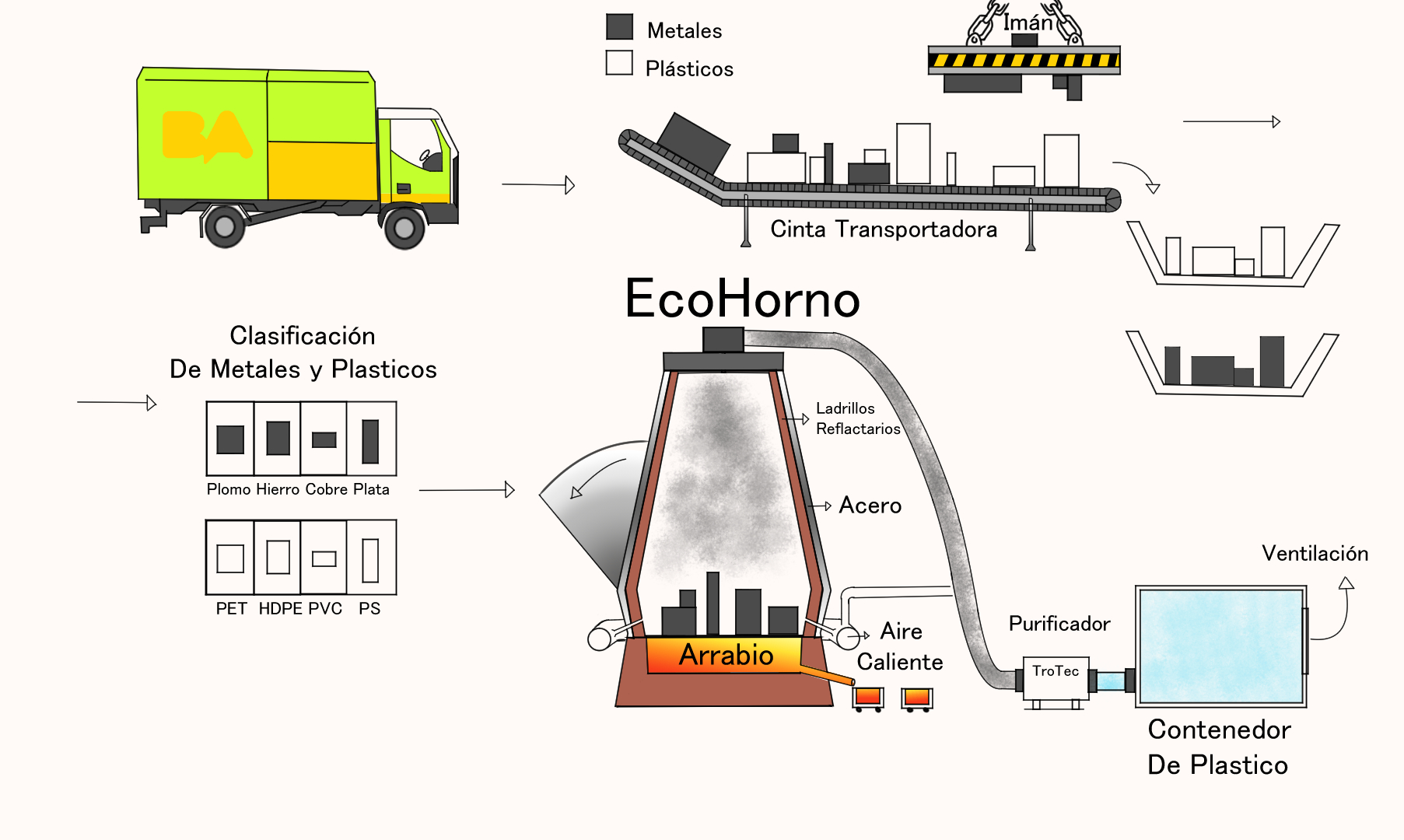
Major supermarkets of the are will be utilized as collection points, where people are going to leave their broken electronic devices or home appliances. They cannot surpass the 2 meters of width or length. Garbage trucks specialized in transporting these kinds of devices, are going to collect once a week the waste left at the collection points. The trucks will take the discarded devices to the factory where the EcoHorno is located.
The truck will deposit the electronic devices and home appliances in a conveyer belt. The magnet placed parallel to the conveyor belt attracts the objects with metal, separating metals from plastics. Components are separated from both metal and plastic objects, removing everything that is toxic or becomes toxic with heat. The metals and plastics are separated according to their classification. They merge separately according to their classification. For the different temperatures in which the components melt:
Copper: 1,050 ° C
Aluminum: 650 ° C
Iron: 1,535 ° C
Silver: 960 ° C
Gold: 1,062 ° C
Bronze: 920 ° C
Nickel: 1,455 ° C
Platinum: 1,770 ° C
Lead: 340 ° C
The metal and liquid plastic, the pig iron, come out from under the furnace and goes to the trucks with the thermal insulators. This takes away the problem of removing the ones inside the oven. Then those trucks are sent to factories that use those metals and/or plastics. The furnace would be used a whole day only for metals, after its last use that day it is cleaned for the next day to use it for plastics. The air purifier is connected directly at the tip of the oven to the floor, where the appliance is going to be, and from the appliance, it goes to the plastic container, which after a little rest is taken out by a ventilation.
Disponibility
The furnace measures 6 meters high and 4 meters in diameter and is made of refractory bricks covered by a steel layer Its production capacity is 1000 tons per day. It has a hot air inlet on the sides of the oven towards the oven that reaches a temperature of 2000 ° C. The temperature is adjustable.
Conveyer belt.
10 meters long and 1 meter wide
Kind: modular
Material: Iron
Width: 160 mm
Industrial Air Purifier
Brand: TROTEC
Model: TAC 1500 S
Length: 61cm
Width: 36cm
Height: 40cm
Industrial magnet
Brand: DIMET
Model: IMG10
1 meter long A
40 cm wide B and
65 cm high C
Weight 1300kg
Weight supported 30 tons
Other Solutions
Other solutions that we found to combat electronic contamination are the following:
Biodegradable batteries: they invented single-use biodegradable batteries based on paper and other organic materials such as beeswax, cellulose and organic redox species such as quinones.
Reuse and revaluation: E-Trash, A group of students, professors and alumni of the University of La Plata carry out a project that consists of gathering electronic devices and trying to repair them, helping not only the environment but also helping disadvantaged institutions of the area giving them those electronic devices that are already in conditions to use. Those that there is no way to repair them and that they are reused are sent to a company with environmental certification for their final and safe disposal, thus avoiding their final stage in burns and garbage dumps. This type of projects is Circular Economy, where things that were broken or malfunctioning are reused.
Green points: In the Autonomous City of Buenos Aires, the number of existing green points was tripled and mobile green points were implemented. What is a green point? They are places where people take Waste Electrical and Electronic Devices to be recycled and properly managed the dangerous components they contain.
Also, a big step forward would be to implement new laws so that each state residence has a safe and well-maintained recycling area. Sweden follows this law and nowadays has managed to recycle 99% of its waste making it one of the greenest countries next to Norway.
